Automating Invoice Review 2024
Invoices are the backbone of B2B transactions, serving as legally recognized documents that validate trade, trigger payments, and facilitate external financing. They play a crucial role in ensuring vendors get paid on time, as payments are directly tied to invoice verification.
ROLE
Product Designer
SECTOR
FinTech
TEAM
Aishwarya Bindana, Ritika Mangate
OVERVIEW
In the B2B ecosystem, invoices are not just transaction records—they govern payments and influence business cash flow. However, invoice processing delays caused by disputes, missing information, and offline issue resolution often resulted in delayed payments for suppliers. This project focused on streamlining invoice review and resolution, reducing manual intervention, and providing a structured, guided approach to handling invoice-related discrepancies.
IMPORTANT TERMS
Credit Note (CN): A document issued to correct overcharges or return goods, reducing the amount payable.
Debit Note (DN): A document issued to request additional payments due to underbilling.
Invoice Hold: A status applied when an invoice requires clarifications, corrections, or approvals before payment processing.
PROBLEM
The invoice review process was highly manual, with no self-serve resolution tools. Users had to manually communicate and reconcile issues via external emails or calls, causing:
21 days
Average time taken to review invoices
40 days
Average delay in resolving invoices placed on hold
30 days
Average delay in supplier payments due
to the time taken in invoice review
to the time taken in invoice review
₹1Cr Annual Cost to Company
An internal team of 7–12 people across 3 teams performing repetitive
tasks due to the absence of a defined SOP and structured validation criteria,
costing the company with low efficiency.
tasks due to the absence of a defined SOP and structured validation criteria,
costing the company with low efficiency.
IMPACT
1. Decrease in Invoice Review Time
Within 1 months, average invoice review came down to 12 and
then 5 days (on the implementation of follow up measures)
Within 1 months, average invoice review came down to 12 and
then 5 days (on the implementation of follow up measures)
2. Reduce Dependency on Internal Users Saving 30-40L Annually
With an automated and structured way of reviewing and resolving invoices, there was a reduction of manpower requirement to 5 people.
With an automated and structured way of reviewing and resolving invoices, there was a reduction of manpower requirement to 5 people.
3. Enable Self-Serve
Increased self-serve actions, leading to fewer offline interactions.
Increased self-serve actions, leading to fewer offline interactions.
4. Faster Supplier Payment
Decreased delay in supplier payments by 23% within 3 months.
Decreased delay in supplier payments by 23% within 3 months.
RESEARCH & INSIGHTS
Main research methods employed were Systemic Data & Workflow Analysis, where we mapped invoice processing steps, highlighting inefficiencies and pain points along with User Interviews to identify key bottlenecks, error handling and matching processes.
1. Redundant Effort Across Teams
Three teams were performing different parts of the same review process manually, leading to repetitive work and wasted effort.
Three teams were performing different parts of the same review process manually, leading to repetitive work and wasted effort.
2. Manual Review Process Leading to Errors
Each user reviewed up to 30 invoices daily, increasing the likelihood of manual errors.
Each user reviewed up to 30 invoices daily, increasing the likelihood of manual errors.
3. No Standardized List of Checks
No set verification list existed, meaning each team followed different validation methods, resulting in lengthy invoice approvals.
No set verification list existed, meaning each team followed different validation methods, resulting in lengthy invoice approvals.
4. Variability in Invoice Structures
Different invoice formats across companies made standardized review difficult, increasing processing time and errors.
Different invoice formats across companies made standardized review difficult, increasing processing time and errors.
5. Manual Adjustments Delaying Processing
Adjustment amounts were calculated manually, causing frequent discrepancies and delays in approvals.
Adjustment amounts were calculated manually, causing frequent discrepancies and delays in approvals.
6. Complex Document Matching Across Systems
Invoice validation required matching against Purchase Orders (PO) and Goods Received Notes (GRN), stored in different system locations, making cross-referencing tedious and error-prone.
Invoice validation required matching against Purchase Orders (PO) and Goods Received Notes (GRN), stored in different system locations, making cross-referencing tedious and error-prone.
7. CN/DNs Created Outside the System
Users generated Credit Notes and Debit Notes externally, causing disruptions in system records and further delays.
Users generated Credit Notes and Debit Notes externally, causing disruptions in system records and further delays.
8. Workarounds & Data Pollution
The system did not support all types of invoice errors, leading users to bypass proper workflows, corrupting data accuracy.
The system did not support all types of invoice errors, leading users to bypass proper workflows, corrupting data accuracy.
HYPOTHESIS
A preemptive, structured, and automated invoice review system will ensure invoices are created correctly from the start, errors are resolved dynamically within the platform, and users can review invoices efficiently with minimal manual intervention. By integrating automated matching, a dynamic resolution calculator, and standardized workflows, we can reduce processing time, increase accuracy, and minimize dependencies on manual follow-ups.
STRATEGY
We opted for a three-fold approach to solve the problem:
→ Preemptively prevent incorrect invoices from being created by enforcing validation checks during invoice creation and upload on the seller end.
→ Assist & automate buyers in reviewing invoices by integrating a document-matching system that cross-verifies invoices with PO and GRN.
→ Enable dynamic resolution and automated note generation within the system to eliminate external processing delays.
SOLUTION
1. Blocking Incorrect Invoices at the Dispatch Stage
Implemented pre-dispatch validation rules to prevent users from generating invoices with missing or incorrect details and matching them preemptively to the purchase order details.
2. Standardized Review Checklist
Created a structured SOP and validation checklist, ensuring that all teams followed a unified review process.
3. Automated Invoice Matching & Assisted Review
Integrated an OCR driven invoice validation system that automatically matches invoices with linked PO and GRN for the buyer to make the review process quicker and more accurate. It also provides corrective action to be taken which will be relayed to the seller. Centralized document access allowed users to review all linked transaction records in one place, reducing cross-system navigation.
4. Train OCR on Different Kinds of Invoices & Allow Buyer to Override System Checks
As the OCR boasts an accuracy of 90-95%, for edge-cases where the OCR is unable to come to a conclusive decision regarding a checkpoint and/or incorrectly marks it, the system allows the final decision to be lay with the user by allowing them to override the check with a corrective description.
5. Real-Time Communication & Status Updates
Implemented invoice hold notifications with clear reasons and resolution steps, reducing manual follow-ups.
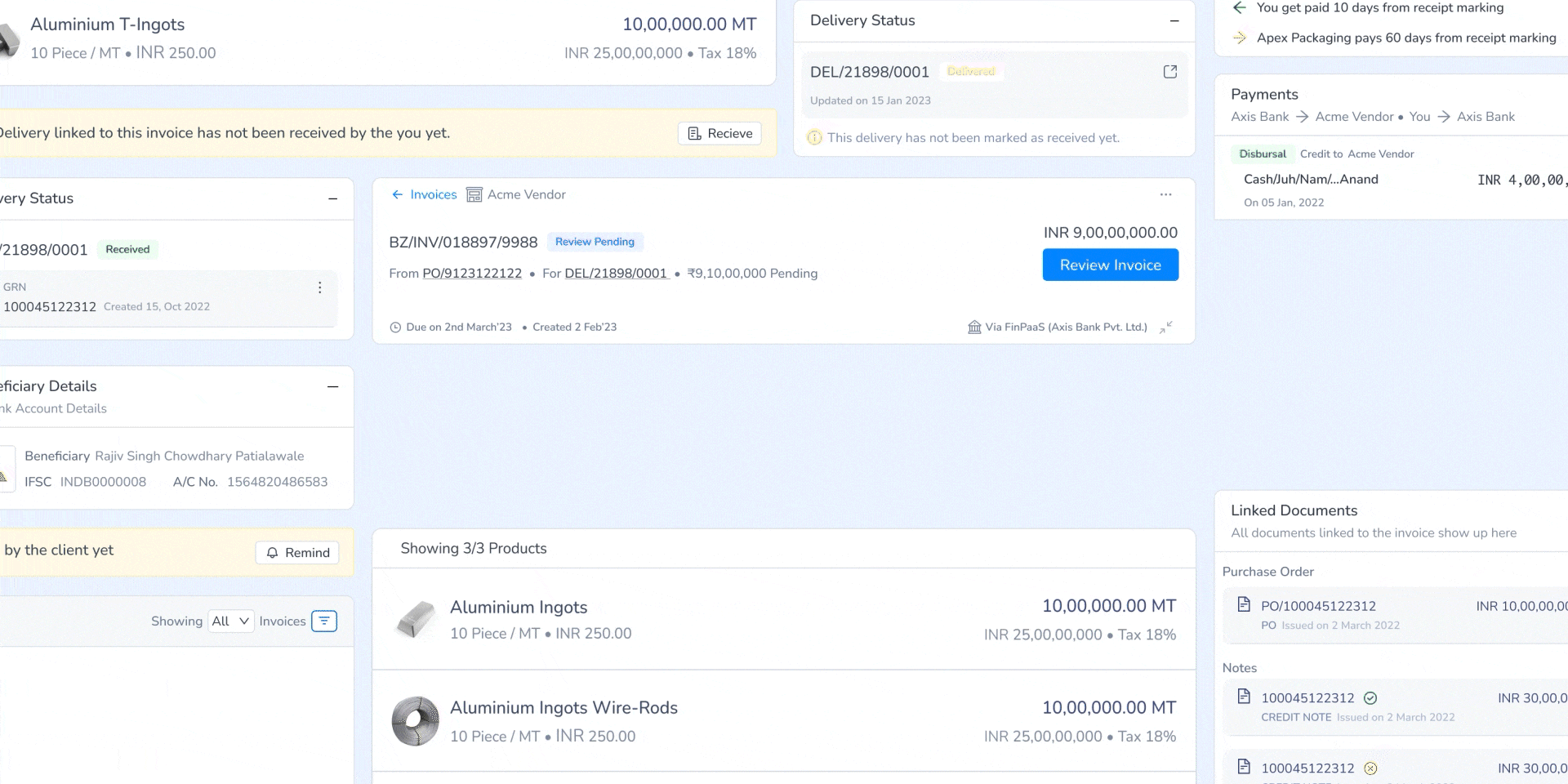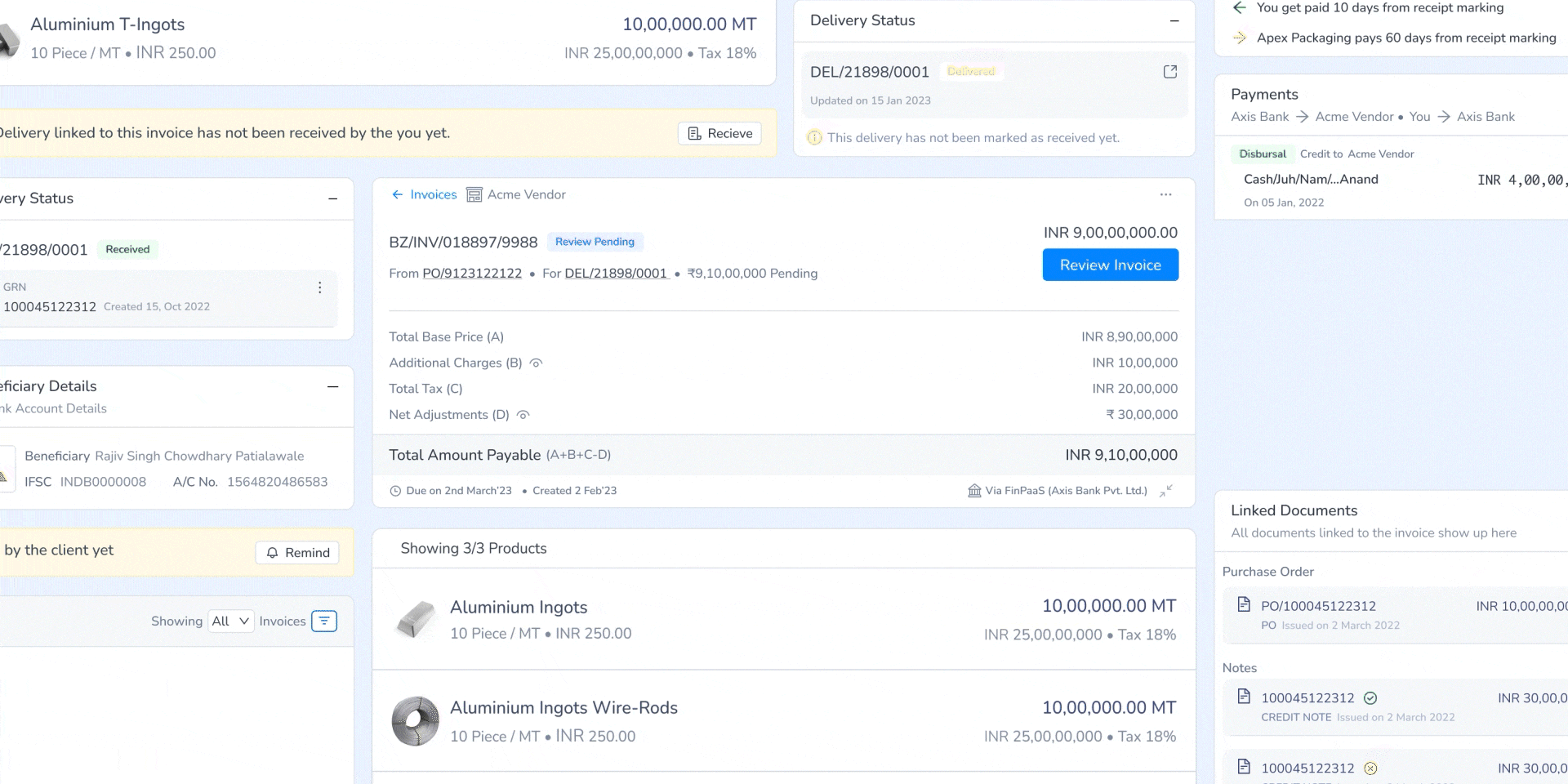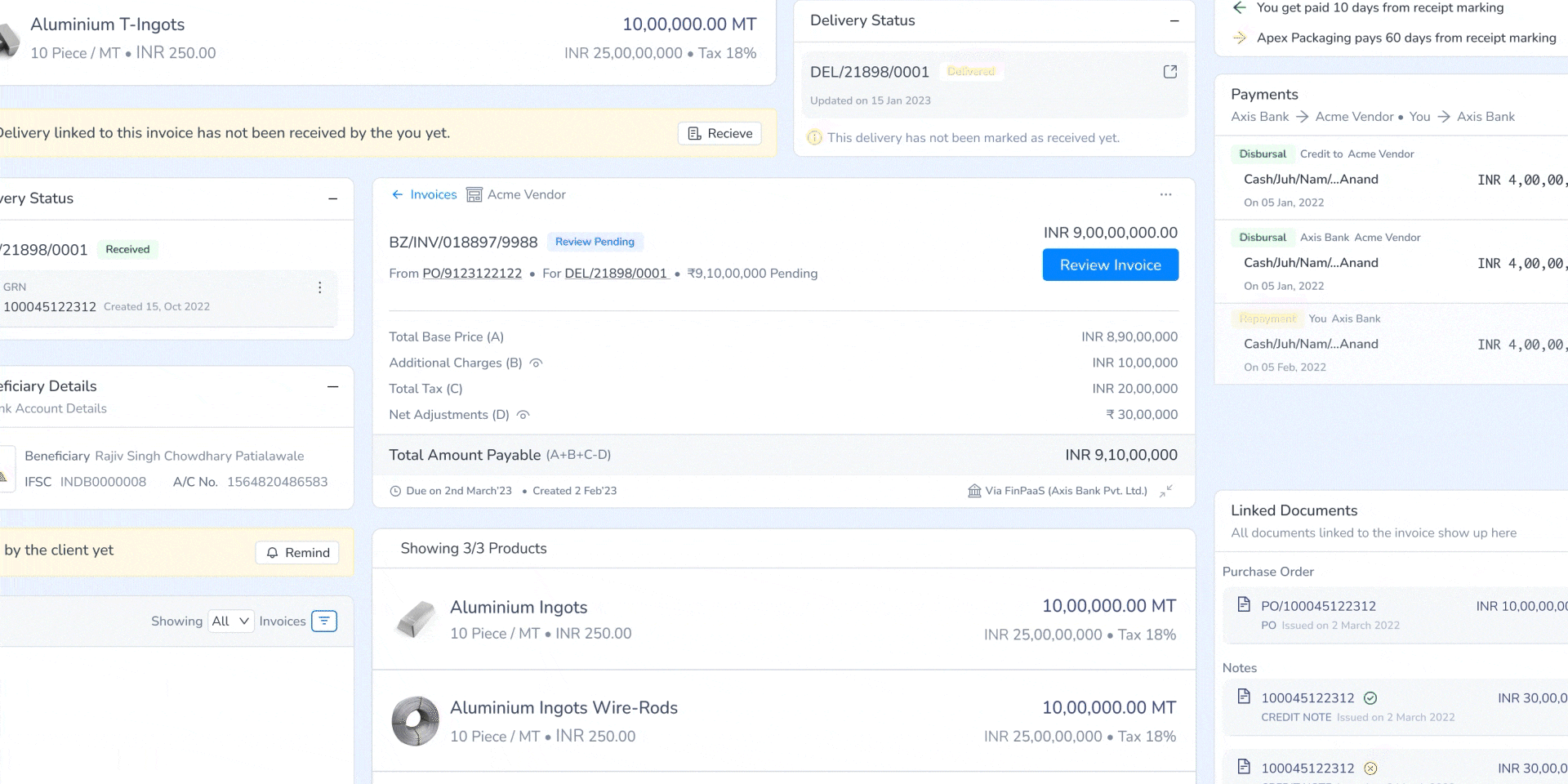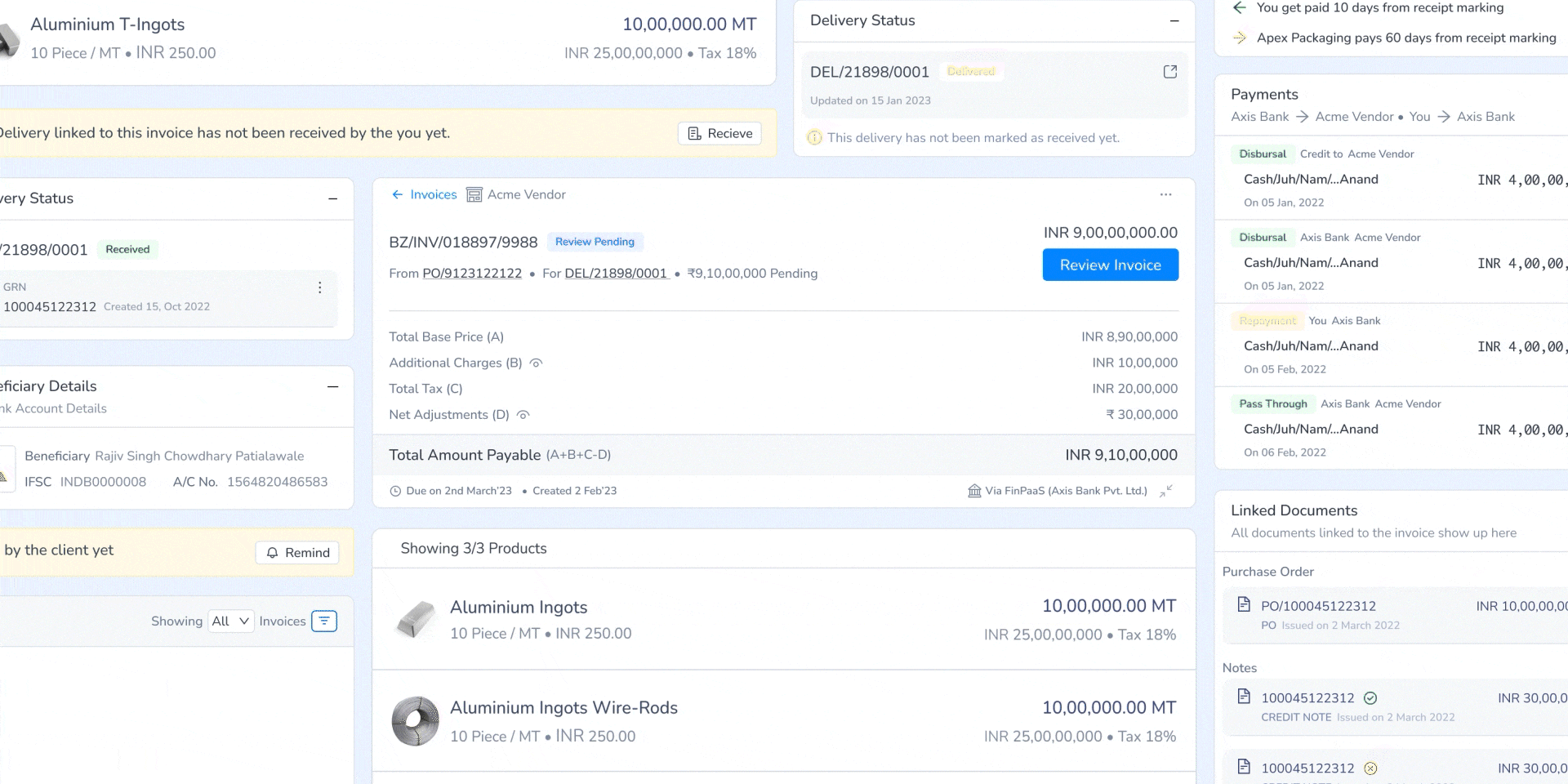
6. Dynamic Resolution Calculator
Introduced a resolution engine that automatically calculates adjustments, eliminating manual computations. Additionally tackled a complex range of problems by standardising them (using historical data on the system) and dividing them based on product impact or overall impact.
7. Automated CN/DN Generation
Enabled one-click CN/DN creation within the system, ensuring correct financial adjustments without external dependencies.
SmartScan was actively tested and is currently being used by internal users. For more details on the enhancements on the process post this, click here