Revamping Invoicing in B2B 2024
Invoices are the backbone of B2B transactions, serving as legally recognized documents that validate trade, trigger payments, and facilitate external financing. They play a crucial role in ensuring vendors get paid on time, as payments are directly tied to invoice verification.
ROLE
Product Designer
SECTOR
FinTech
TEAM
Aishwarya Bindana
OVERVIEW
However, the existing invoice page lacked structured navigation, real-time tracking, and adaptability across business models, making it difficult for users to track payments, validate deliveries, and take timely actions. This project aimed to redesign the invoice page to enhance usability, ensure responsiveness, and provide actionable insights to improve invoice processing efficiency.
IMPORTANT TERMS
Invoice: A legally binding document that records a sale, including transaction details, payment terms, and obligations of both parties.
On-Hold Invoice: An invoice flagged due to missing details, disputes, or pending approvals, delaying processing.
Linked Transactions: Invoices are directly connected to order status, delivery tracking, and payments, making them a key financial control point.
PROBLEM
Invoice management within the platform was inefficient, lacking clarity, automation, and self-service functionalities, leading to delayed payments, manual workarounds, and heavy dependency on offline communication.
Managing invoices efficiently—especially in a complex ecosystem with multiple business models—poses a significant challenge.
Invoice pages were the second most visited section in the portal, accounting for 52% of total interactions yet the average time spent on an invoice page was 12 seconds highlighting that crucial, important actions were being performed off the system.
IMPACT
1. Improved Engagement & Interaction
Within 3 months, there was a 32% reduction in user
drop-off rates from invoice pages.
Within 3 months, there was a 32% reduction in user
drop-off rates from invoice pages.
2. Reduce Invoice Review Time & Quicker Payments
Automations led to quicker payments, reducing supplier payment delays by 16 days.
Automations led to quicker payments, reducing supplier payment delays by 16 days.
3. Enable Self-Serve
Increased self-serve actions, leading to fewer offline interactions.
Increased self-serve actions, leading to fewer offline interactions.
4. Better Navigation & User Guidance
The new structure provided better guidance leading to 75% reduction in dead-clicks by users.
The new structure provided better guidance leading to 75% reduction in dead-clicks by users.
RESEARCH & INSIGHTS
Main research methods employed were Systemic Data Analysis, where we studied user behaviour, time spent on invoice-related tasks, and resolution timelines and User Interviews aimed at gathering insights from buyers and sellers about challenges faced in invoice management.
1. Poor UX & Ambiguity in Steps
No clear CTAs (Call-to-Actions) & the page presented too much data without clear structure, making it difficult to extract relevant details leading to confusion & 67% dead-clicks.
No clear CTAs (Call-to-Actions) & the page presented too much data without clear structure, making it difficult to extract relevant details leading to confusion & 67% dead-clicks.
2. Lack of Clear Feedback
Users had trouble tracking payments against invoices, making reconciliation cumbersome. 23% of users had to check multiple sections to confirm payment status.
Users had trouble tracking payments against invoices, making reconciliation cumbersome. 23% of users had to check multiple sections to confirm payment status.
3. Manual Dependency for Calculations of Payable Amounts
Invoice validation depends on delivery completion, yet delivery status was missing, leading to delays in invoice matching.
Invoice validation depends on delivery completion, yet delivery status was missing, leading to delays in invoice matching.
4. Unable to Cater to Different Business Models in a Scalable Manner
Both users and the system were not able to distinguish and adapt to newer models of business which called for different lifecycles of an invoice.
Both users and the system were not able to distinguish and adapt to newer models of business which called for different lifecycles of an invoice.
5. Missing Bank Account Details
Users had no visibility into linked bank accounts, making it difficult to validate payments.
Users had no visibility into linked bank accounts, making it difficult to validate payments.
6. No Real-Time Updates on Invoices Put on Hold
Invoices placed on hold had no immediate notifications or reasons displayed, forcing users to rely on external communication. Average time to resolve invoices on system was 21 days.
Invoices placed on hold had no immediate notifications or reasons displayed, forcing users to rely on external communication. Average time to resolve invoices on system was 21 days.
7. Non-Responsive Layout
The invoice page was not optimized for mobile or tablet usage, limiting accessibility across devices considering 14% of our users used mobile to monitor status of invoices.
The invoice page was not optimized for mobile or tablet usage, limiting accessibility across devices considering 14% of our users used mobile to monitor status of invoices.
Status Cycle Map
Mapping User Flows for All Use Cases
HYPOTHESIS
A structured, responsive, and progressive disclosure-driven invoice page will enable users to quickly track payments, validate invoice status, and take corrective actions in real time, process invoices efficiently and reduce dependency on external communication.
STRATEGY
Redesign the information architecture to create a clear, structured, and action-driven invoice experience. Integrate critical financial and transactional data seamlessly while providing contextual actions and guided user flows that help users track payments, resolve issues, and take necessary actions with minimal effort.
SOLUTION
By prioritizing key insights, linking related transactions, and enabling self-serve rectifications, the new design ensures faster decision-making and reduced dependency on external communication.
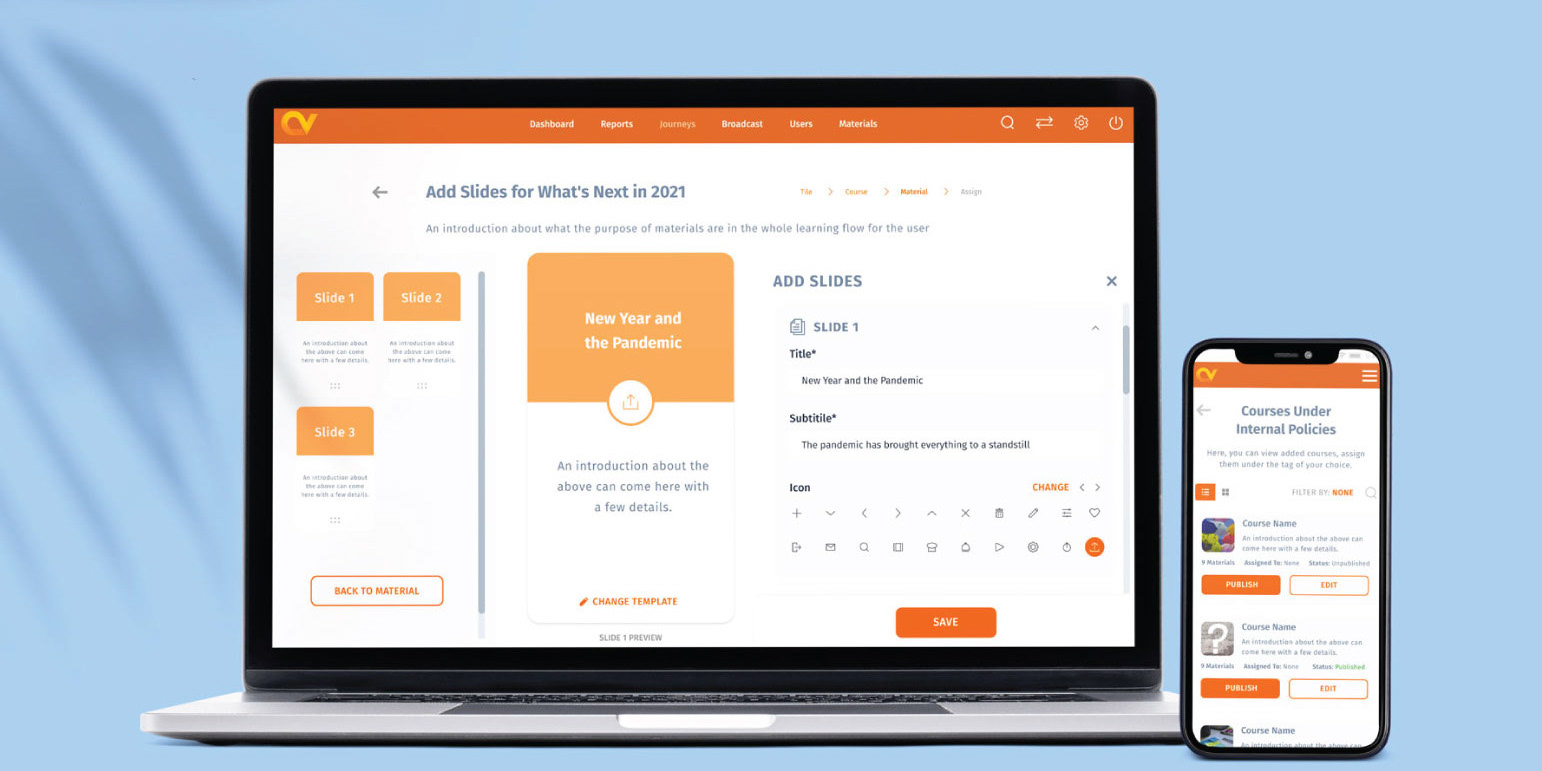
1. Streamlined Overall Information Architecture
• Broke down invoice information into logical sections to allow retrieval of critical information faster and action on necessary items without confusion.
• Restructured information hierarchy, surfacing critical details upfront while keeping secondary information accessible.
• Implemented inline actions that allow users to take necessary steps without leaving the page.
2. Dynamic Invoice Status Cycles for All Business Model
Identified unique workflows across different business models and mapped their invoice processing needs to ensure adaptability and introduced a dynamic invoice status cycle adaptable to various business models along with tags to differentiate, ensuring clarity at every stage.
3. Responsive Card-Based Layout for Streamlined Usability
Moved to a modular card-based structure, ensuring a clean, organized layout adaptable across devices.
4. Progressive Disclosure for Better Navigation
Reduced cognitive load by grouping relevant actions and prioritizing key invoice attributes using accordions.
5. Real-Time Payment & Status Tracking
• Integrated real-time payment tracking to ensure users can instantly verify transaction status.
• Added delivery status updates for accurate invoice matching and faster approvals.
6. Visibility into Linked Bank Accounts
• Displayed linked bank account details within the invoice for easier payment validation.
• Enabled inline verification prompts, reducing errors in financial reconciliation.
7. Inline Invoice Adjustments & Dispute Handling
Enabled OCR review technology and in-system issue resolution, allowing users to correct discrepancies without the need for external follow-ups.
Know more about this here.
8. Payment Terms Mapping & Automated Reminders
Linked payment terms to invoices, triggering timely reminders for upcoming due dates and improved cash flow planning by alerting users to pending payments before deadlines.